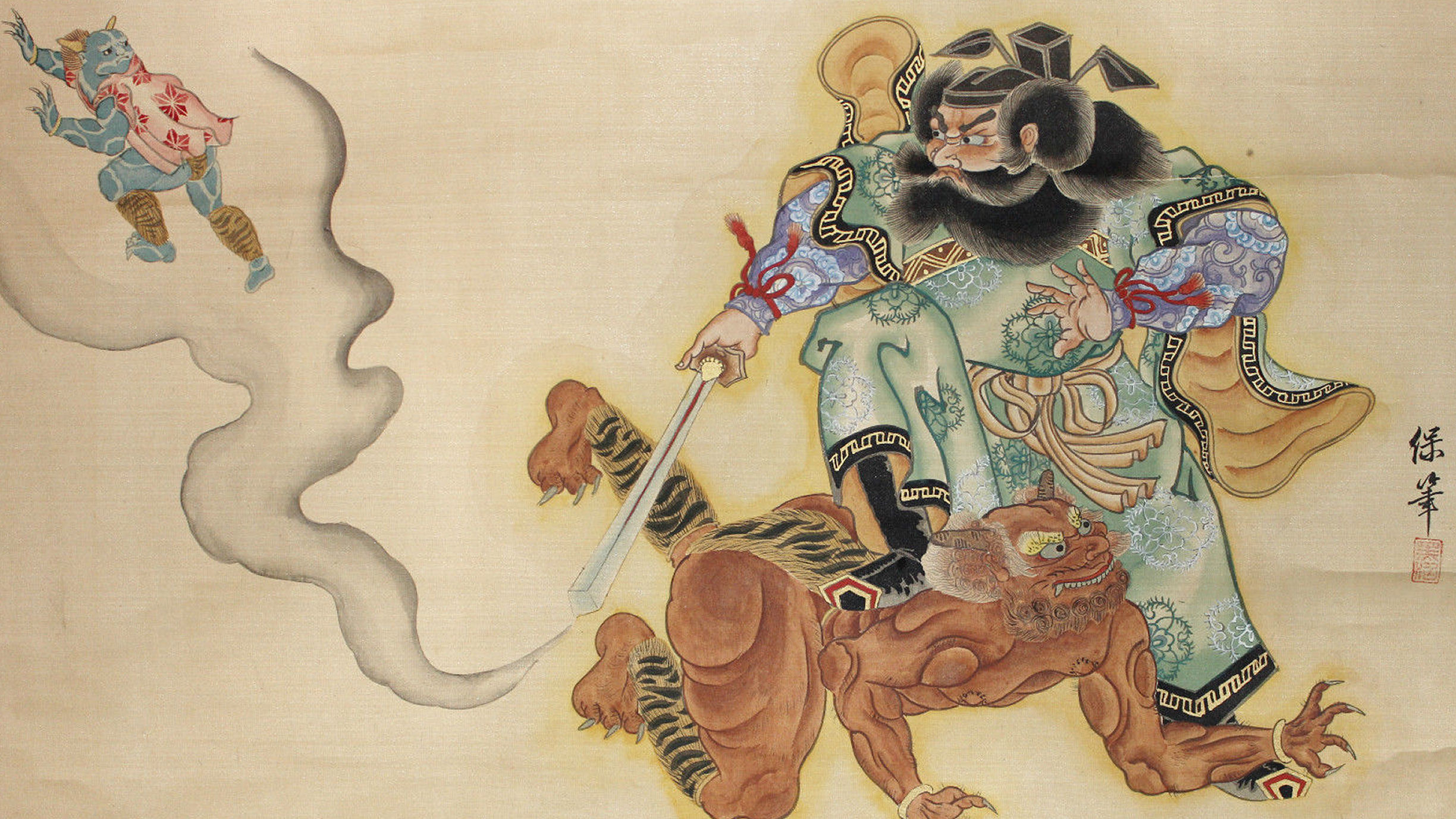
I stumbled upon an online discussion criticizing Fabrizio Pregadio’s translation of gui 鬼 to “demon, devil” [in Encyclopedia of Taoism (2008)], calling this translation inaccurate and problematic. The commenters in that discussion thread preferred the translation of gui to “ghost,” emphatically declaring that gui as ghost is the right approach, and that equating gui to demon or devil is wrong.
The rationale was that demon and devil have a connotation of evil in the West, which the term gui does not have. The term “ghost” is a bit more neutral – they say – and so gui as ghost is the better translation.
Continue reading “The Semantics of Devil, Demon, and Ghost: 鬼 Guǐ”