$40
A Cultivation Practicum
This is an introduction to Taoist inner alchemy, by way of cultivation work with the Zhou Tian, or Mandalas of Heaven, grounded in canonical source texts and living tradition. Key features of this curriculum are:
- A 200+ page structured textbook and workbook (that serves as a companion and book of your study notes, personal reflections, and log of experiences)
- Primary canonical texts translated into English (I don’t believe I’ve ever seen this obscure text translated into English before) with annotations
- Practice instructions that go beyond the free, publicly available lectures and guided experience prompts
- Structures the free, publicly available material into theoretical foundations and practical application
- Emphasis on ethical grounding and safety
- Participant Question & Answer feature (a password-protected FAQs page tailored to you)

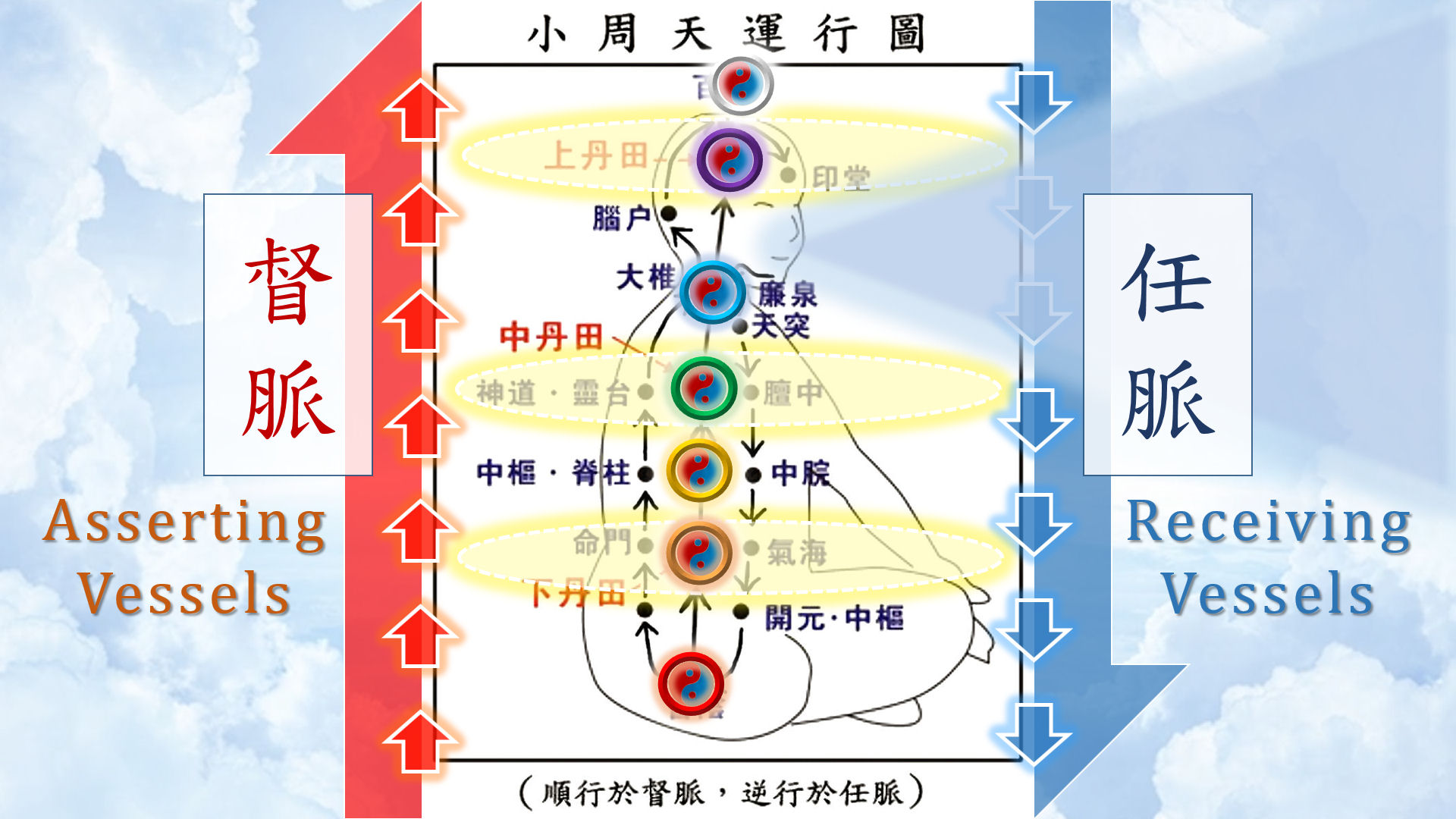
The two core lectures on the Lesser Mandala of Heaven 小周天 and Greater Mandala of Heaven 大周天 are already available free to the public, which you can access:
- A Taoist Secret to Cultivating Personal Power: On the Lesser Mandala of Heaven, Xiao Zhou Tian 小周天
- Video Lecture
- Supplemental Notes
- Advanced Introduction to Taoist Alchemy: On the Greater Mandala of Heaven, Da Zhou Tian 大周天
- Video Lecture
- Supplemental Notes
This deeper-dive cultivation practicum organizes what was introduced in those two lectures into a sequential system that becomes praxis-oriented.
The course book, which is a workbook, is a guide on how to integrate those core practices.
In other words, the two free lectures introduce the ideas. This course is where the cultivation actually happens. It is a structured container for the teachings.
The coursework expands the scope in depth and breadth, curating a curriculum to study, practice, and self-reflect on the Mandalas over a period of 100 days, guided by a 200-page course textbook, through which you will:
- Notably increase your internal vitality, awakening and actualizing otherwise untapped core powers, &
- Master the foundational principles and symbolic systems shared among many lineages of folk magic across Asia, essential in Taoist mysticism and esoteric Buddhism.
Deliverables
- A 200+ page cultivation manual and workbook (digital PDF delivered to your email inbox; you can order a printed spiral-bound copy of the book via a third-party print-on-demand site at-cost). Your course text becomes your one-stop consolidated resource with all of the following and more:
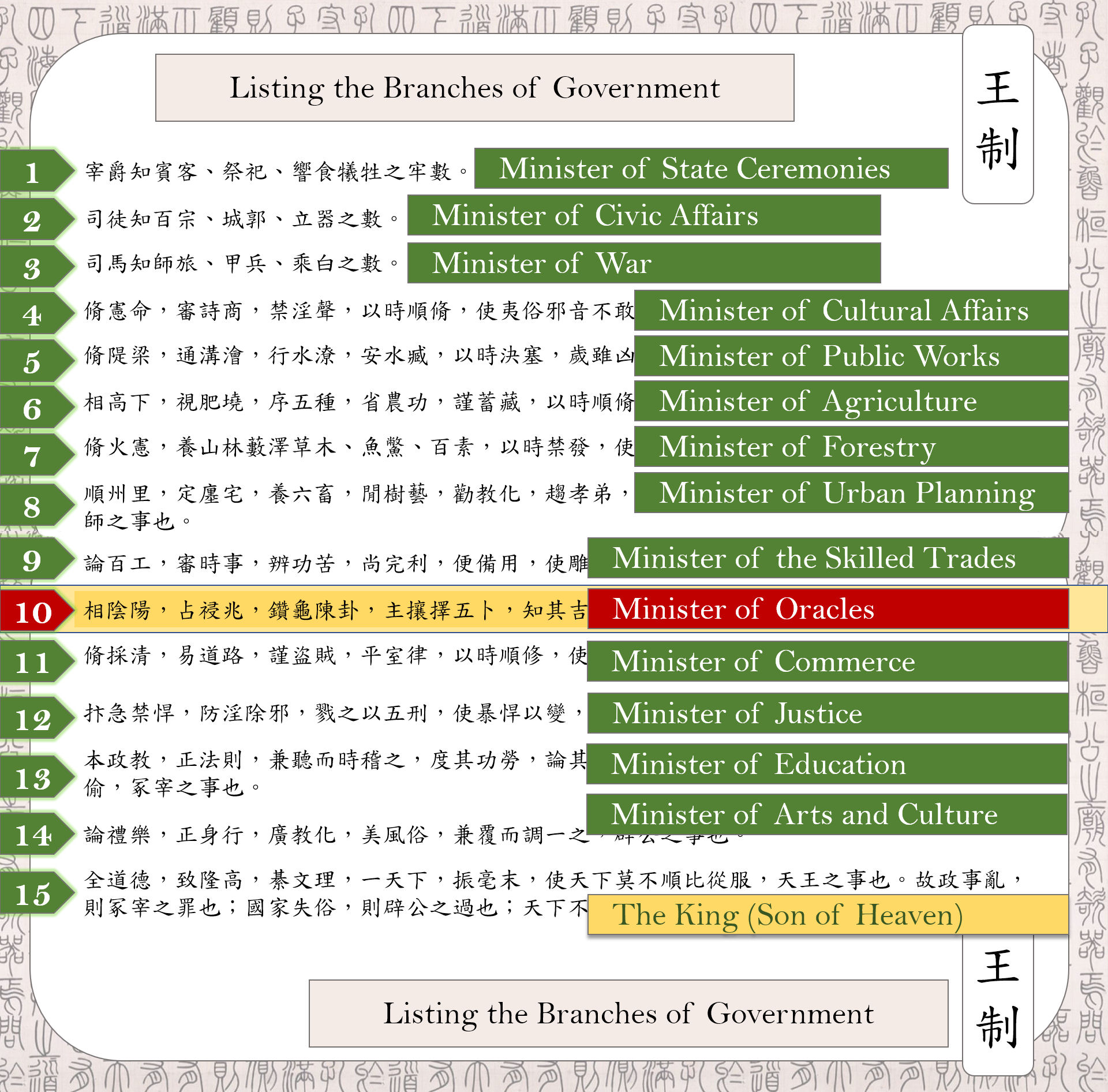
- Authoritative reference tables and diagrams
- Organized sections with clear, beginner-accessible explanations of core Taoist principles, especially in the area of inner alchemy
- Step-by-step guided practice instructions
- Canonical sources and textual translations, so that you know where these practices come from and how they were historically understood
- Reflection prompts and line space for you to log your insights and experiences right next to the reference materials– this helps to reinforce your learning, and also serves as a journal– you’ll be able to refer back what you wrote in here and assess your own progress
- MP4 downloads of just the guided meditation. I’ll send you two versions: one that has Heart Sutra musical incantations in the background layered beyind my voiceover narration, and a version that’s the voiceover narration only.
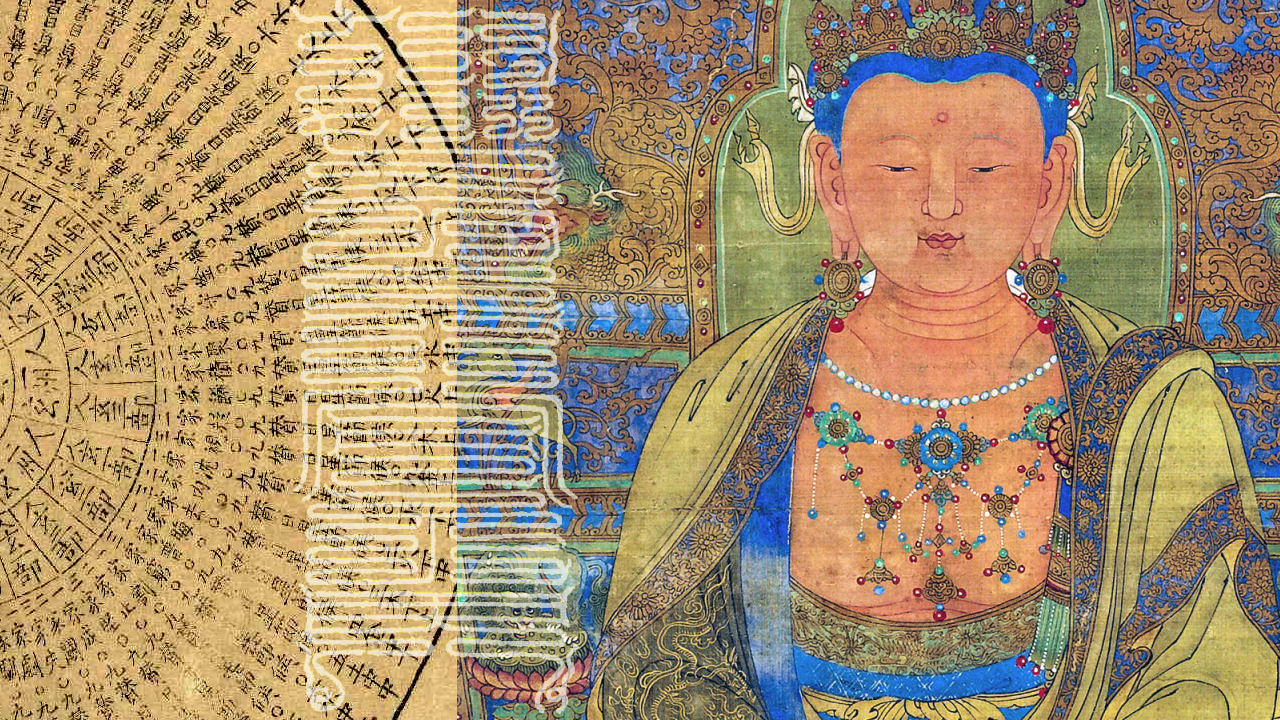
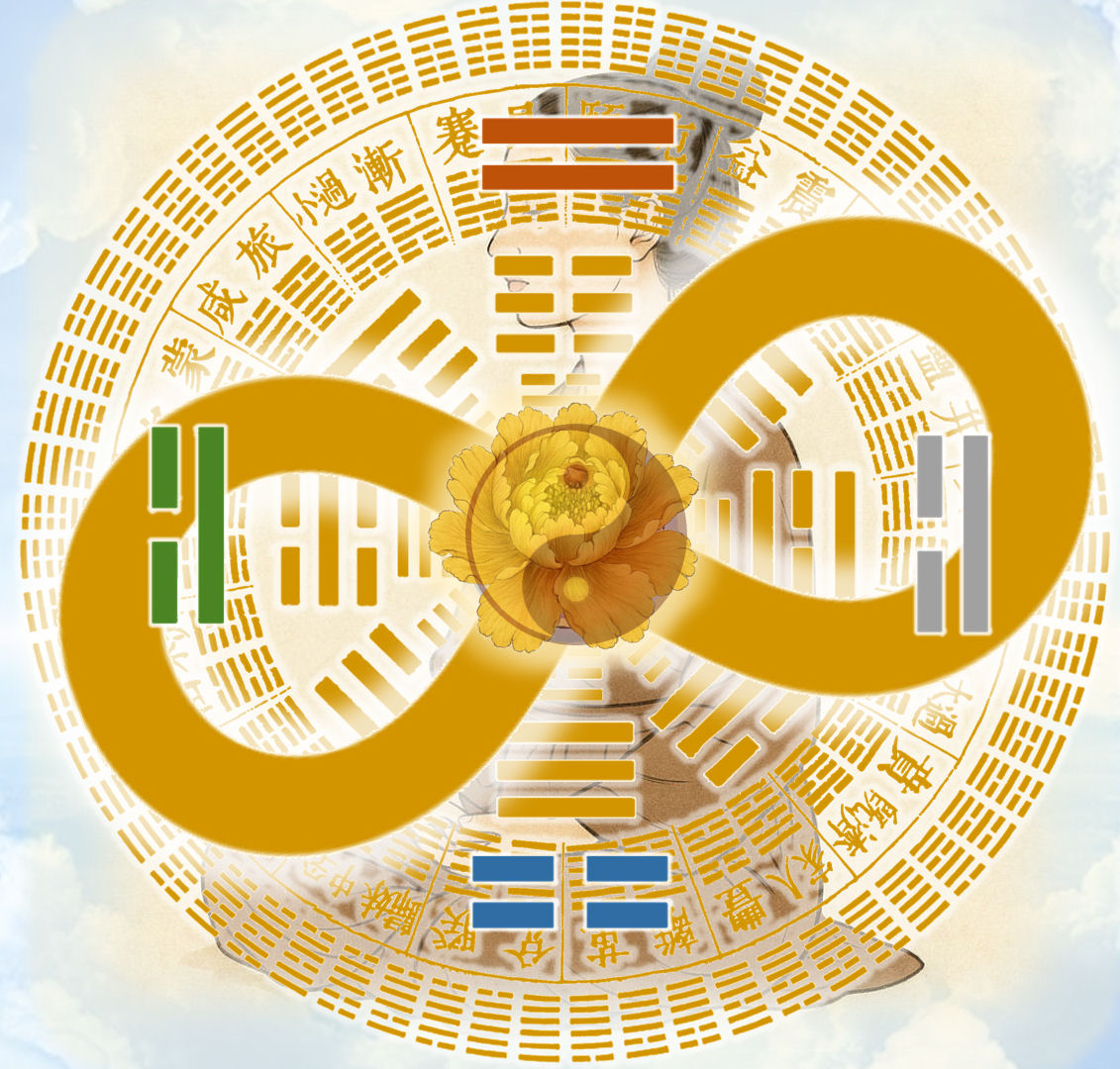
- 300-dpi resolution digital image of the cover design (17.25” x 11.25”), which can be be used for art prints, wall hangings, etc. In Taoist and various Eastern esoteric traditions, such a design would be called a form of Spirit Map (靈圖, líng tú) or magical painting (術畫, shù huà).
- Cover design features four mandalas from the post-Geluk era (circa 17th c.) representing the canonical four Buddha families and generally symbolic of a four-fold cosmological system of protective guardians.
- The central seal that spreads across both the front and back covers is the Blue Medicine Buddha. The 64 hexagrams appear both as an 8×8 square diagram and as a full circle.
- Original translations and annotations of excerpted chapters from the Dao Men Yu Yao 道門語要 (Fundamentals of Taoist Alchemy), circa 1271 – 1325, specifically the two chapters on the Lesser Mandala “運小周天之法” and the Greater Mandala “行大周天之功” with explanatory annotations
- Fundamentals is a collection of much older canonical essays compiled by Huang Shang 黃裳, a Taoist priest of the Zhongpai 中派 (Middle Pillar Lineage), a tradition of Taoist inner alchemy
dated back to the Yuan dynasty founded by the master Li Daochun 李道纯.
- The essays date back to the Yuan dynasty, received texts of the Lineage, while the date of Huang Shang’s compilation is unclear, though speculated to be the Qing dynasty.
- The Middle Pillar Lineage was known for its syncretizing of Taoism, Buddhism, and Confucianism.
- The term “黃裳,” Huang Shang’s namesake, is a direct reference from Hexagram 2, Line 5 of the I Ching.
- QUESTION & ANSWER WITH BELL | Course Participants Only FAQs Page. Email me your questions and I’ll compile the Q&As into a password-protected page for course participants only. This is your opportunity to ask me any questions you have related to these subjects.
- Admittedly I’m not great at responding to emails, especially ones with questions that may involve a thoughtful, thorough reply. But the questions submitted through this course curriculum will be prioritized, and I’ll answer them via multimedia formats on a password-protected FAQs page.
- You can ask anything related to this subject matter. Or ask how I personally practice, or apply certain principles. Feel free to ask about my perspective, or ask the questions on Taoist mysticism that you can’t seem to find anywhere else in English.

Download the
Through the framework of the Lesser and Greater Mandalas of Heaven, this course introduces the foundations of classical Taoist inner alchemy. It will consist of studying translations and annotations of canonical source texts on the Mandalas of Heaven, guided practice, and reflective work.

Download an Excerpt
For a sampling of what’s in the course book, click on the above link to a PDF to read the first 49 pages, which outlines your learning objectives, gives you the table of contents, and introduces the premise of this Work.
Continue reading “Mandala of Heaven 周天: Taoist Alchemy Course” →